Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Causes of Aging Skin Under Chin Fillers
Causes of aging skin under chin fillers can be attributed to various factors, including
- Loss of fat and volume in the submental area
- Gravity’s effect on the skin, causing it to sag and droop over time
- Age-related changes in skin elasticity and texture
- Genetic predisposition to premature aging
- Hormonal fluctuations, particularly with decreased estrogen levels during menopause
In addition to these factors, the distribution of fat in the face can also play a role in the appearance of aging under chin fillers.
A well-distributed and harmonious facial fat profile is crucial for creating a natural and youthful appearance. When fat is evenly distributed across the face, it helps to:
- Fill out hollows and contours, giving the face volume and depth
- Cream over bony structures, making them less visible
- Smooth out fine lines and wrinkles, creating a more refined and smooth appearance
On the other hand, when fat is concentrated in one area or is unevenly distributed, it can create an unnatural and aged appearance under chin fillers.
This is particularly true if the fillers are placed in a way that accentuates a lack of volume in the submental area, rather than complementing the existing facial structure.
In order to avoid a prematurely aged appearance after chin fillers, it’s essential to consider the role of fat distribution and structure when selecting a qualified and experienced provider.
A provider who takes the time to understand the unique needs and anatomy of each patient can help create a customized treatment plan that addresses
- Fat preservation and augmentation strategies
- Subcutaneous tissue management
- Cosmetic contouring techniques
By addressing these factors, patients can enjoy more natural and long-lasting results from their chin fillers, and avoid the premature aging of skin under the treatment area.
The placement of chin fillers can lead to a less than flattering appearance due to an unnatural shape, which can accentuate fine lines and wrinkles in the face.
Aging skin under the chin, also known as a double chin or submental fullness, is caused by a combination of factors including genetics, weight gain, poor posture, and loss of facial fat.
When fillers are placed too high on the chin, they can create an unnatural silhouette, making the face appear longer and more pointed than intended.
This can be particularly noticeable when the underlying fat distribution is uneven, leading to a lopsided or asymmetric appearance.
The chin area contains a layer of muscle called the platysma, which runs from the chin to the neck and plays a role in the aging process.
As we age, the muscles in our face begin to weaken, including the platysma, leading to a droopy or sagging appearance under the chin.
Filler placement can sometimes push fat upwards towards the chin, creating an unnatural bulge that accentuates fine lines and wrinkles on the face.
Aging skin is also more prone to bruising and swelling after filler injections due to decreased collagen production and a thinner dermal layer.
Furthermore, the jawline and facial structure become less defined with age, leading to an increased appearance of sagging under the chin.
The effects of aging skin can be further exacerbated by factors such as gravity, loss of fat, and muscle weakness, all of which contribute to a less than desirable appearance when fillers are placed incorrectly.
Additionally, the chin area is highly sensitive due to its proximity to the mouth and nose, making it more susceptible to bruising and swelling after filler injections.
This can lead to an unnatural and asymmetrical appearance, particularly if the placement of the fillers is not carefully considered in relation to the underlying facial structure.
The risk of complications also increases with the use of chin fillers by inexperienced practitioners or those who do not fully understand the nuances of facial anatomy and aging skin.
Aging skin under the chin, also known as submental wrinkles or folds, can be a significant concern for individuals undergoing facial rejuvenation treatments, including chin fillers. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, a lack of submental fat can contribute to the appearance of longer and more aged faces.
The study highlights that the submental area is a common site for wrinkles and folds due to the loss of fatty tissue with age. As we lose fat in this region, it can lead to the formation of deep wrinkles and creases under the chin, creating an older appearance. In fact, the researchers found that patients who had lost significant amounts of submental fat tended to have more pronounced facial aging signs, including nasolabial folds and marionette lines.
Several factors contribute to the loss of submental fat with age, including:
- Genetics: Inheritance plays a significant role in determining one’s facial structure and fat distribution, which can affect the appearance of aging skin under the chin.
- Aging skin elasticity: As we age, our skin loses its natural elasticity, leading to the formation of wrinkles and folds, including those under the chin.
- Loss of submental bone structure: The submental bone plays a crucial role in supporting fatty tissue in this region. As we age, the bone structure can weaken, contributing to the loss of fat and the appearance of aging skin.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menopause or andropause can lead to increased fat redistribution, including a decrease in submental fat.
- Weight gain or loss: Significant weight gain or loss, particularly around the midface and neck, can alter facial proportions and create the appearance of aging skin under the chin.
The researchers suggest that addressing the underlying causes of submental fat loss is essential for achieving optimal results with chin fillers. By understanding these factors and taking a comprehensive approach to facial rejuvenation, individuals can minimize the appearance of aging skin under their chin and maintain a more youthful appearance.
Cause and Effect Relationship Between Chin Fillers and Aging Skin Under the Chin
A popular cosmetic procedure, chin fillers aim to enhance the definition of the jawline, reduce a double chin, and improve overall facial contours.
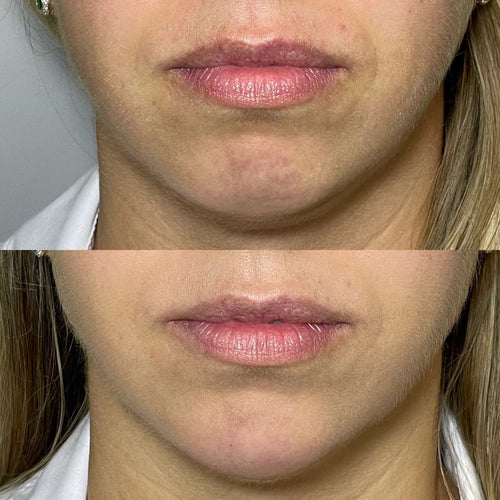
However, beneath the surface of a more defined lower lip and reduced jowling, some patients may notice that their aging skin under the chin is not addressed by the procedure alone.
The primary cause of aging skin under the chin can be attributed to various factors beyond the scope of chin fillers. One key contributor is the loss of submental fat.
Submental fat refers to the layer of fatty tissue located beneath the chin, and its depletion with age leads to a hollow or gaunt appearance under the chin, which is more noticeable when accentuated by chin fillers.
Another factor that can lead to puffy or sagging skin under the chin is gravity’s effect on loose facial skin. As we age, our skin’s elasticity decreases, causing it to lose its firmness and lift.
This loss of elasticity allows gravity to pull down, creating folds and wrinkles under the chin, particularly in individuals who have experienced significant weight fluctuations or sun damage.
A weak or absent platysma muscle also plays a role in contributing to aging skin under the chin. The platysma muscle is a thin, fan-shaped sheet of muscle that runs from the lower lip to the chest wall; its atrophy can lead to a sagging appearance under the chin.
Genetics and smoking are additional factors that can negatively impact facial skin tone, leading to premature aging under the chin. Smoking, in particular, damages collagen production and depletes oxygen supply, accelerating facial aging.
Additionally, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions such as hypothyroidism or autoimmune diseases can lead to the accumulation of fat under the chin, further exacerbating a puffy appearance.
Awareness of these underlying causes highlights that while chin fillers can provide temporary solutions to address volume loss and redefine the jawline, addressing the root causes of aging skin under the chin is crucial for long-term results.
Combining chin fillers with other treatments tailored to the individual’s specific needs can help minimize fine lines, wrinkles, and folds under the chin, ultimately leading to a more youthful appearance.
How Chin Fillers Affect Facial Contour
The placement of hyaluronic acid or other fillers into the submental area, which lies beneath the chin, can significantly impact facial contour and overall facial balance. When done correctly, this procedure can enhance the appearance of a smaller, more defined chin, creating a more balanced and harmonious face.
However, when executed incorrectly or in excess, chin fillers can accentuate a receding chin, leading to an unbalanced look that may make a person appear older. This is because the fillers are attempting to augment a weak or absent chin structure, rather than working with the natural anatomy of the face.
The relationship between the chin and facial balance is complex, as it involves not only the shape and size of the chin but also its position in relation to the nose, cheeks, and forehead. A well-proportioned face is one where each feature is balanced relative to the others, creating a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing whole.
In terms of facial balance, the chin plays a crucial role in offsetting the weight and gravity of the lower face. A strong, defined chin helps to counterbalance the soft tissues of the neck and jawline, preventing them from sagging or drooping prematurely. When a receding or poorly filled-in chin is present, this balance can be disrupted, leading to an aged appearance.
Additionally, the chin’s position relative to the nose and mouth also affects facial balance. A well-aligned nose and mouth are critical components of a harmonious face, as they serve as key anchors for the rest of the features. When these facial landmarks are out of alignment, it can create an unbalanced look that detracts from the overall appearance of the face.
Furthermore, facial age can be perceived even when chronological age is low due to the cumulative effects of loss and changes in soft tissue over time. Fat pads under the chin naturally decrease with age, leading to a more pronounced definition between the bottom of the neck and chin, creating the illusion of an older face.
Chin fillers can affect facial contour by altering the perceived volume, shape, or position of the chin, which in turn influences the overall balance and aesthetic appeal of the face. The success of these treatments depends on accurate anatomical knowledge and technical skill, ensuring that the fillers are placed at the optimal depth and location to achieve a youthful, balanced appearance.
Ultimately, when done correctly, chin fillers can enhance facial contour without making one appear older. A combination of proper patient selection, meticulous technique, and realistic expectations is essential to achieving a harmonious face that looks naturally refreshed and revitalized.
The administration of **chin fillers** can significantly impact facial contour, and when done incorrectly, it can lead to an aesthetically less-than-ideal silhouette.
When **chins are filled**, the primary goal is to restore lost volume, enhance the overall appearance, and create a more defined jawline. However, if not administered correctly, the results can have unintended consequences on facial balance and aesthetics.
A well-executed **chin filler** treatment involves careful consideration of individual facial structure, bone density, and skin elasticity. The procedure requires a thorough understanding of human anatomy and a meticulous approach to avoid over-filling or under-filling the area.
When **chins are filled too much**, it can lead to an unnatural appearance, where the chin appears oversized or protrudes excessively from the rest of the face. This can be particularly problematic for individuals with an already prominent jawline or angular facial features.
In such cases, the **facial balance** is disrupted, creating a less-than-stylish silhouette that may draw attention away from other facial areas. The result can appear aged, tired, or even **sagging**, as the overall harmony of the face is compromised.
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Furthermore, over-filling can also accentuate existing **facial asymmetry** issues, such as a crooked nose or uneven cheekbones. In these situations, **chin fillers** may exacerbate the problem, making it more challenging to achieve a natural-looking result.
On the other hand, under-filling can lead to an unfulfilled desire for a more defined jawline. This can result in an unbalanced appearance, where the chin seems too small or **non-existent**, leading to an overall less-than-satisfactory outcome.
To achieve optimal results with **chin fillers**, it’s crucial to find a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon who has extensive experience in administering these treatments. They will work closely with you to determine the most suitable treatment plan, taking into account your individual needs and facial structure.
A thorough pre-treatment consultation is vital to discuss expectations, review **facial anatomy**, and establish a personalized treatment strategy. This ensures that the **chin filler** procedure is tailored to meet specific goals and desired outcomes.
Additionally, it’s essential to follow post-treatment guidelines carefully to minimize risks of adverse reactions, such as bruising or swelling. A well-informed patient can also better manage their expectations and appreciate the importance of patience during the healing process.
Ultimately, **chin fillers** can be an effective solution for restoring lost volume and enhancing facial contour when administered correctly. However, when done incorrectly, they can lead to a less-than-desirable outcome that detracts from overall facial appearance and may even make one appear older than desired.
By understanding the importance of proper technique and individualized treatment planning, individuals can enjoy a more natural-looking result that enhances their unique features and contributes positively to their overall sense of self-confidence.
A well-placed chin filler can enhance the definition of the jawline and facial contour, giving the face a more youthful appearance.
However, if the filler is placed incorrectly or in excess, it can have the opposite effect and create an unnatural look that draws attention away from the desired result.
A “stubby” or “puffed-up” appearance, as described by Dr. Michael Goldfarb, associate clinical professor at UCLA Medical School, is a common consequence of poorly placed chin fillers.
This can occur when too much filler is injected into the area, causing it to become swollen and unnatural in shape.
Alternatively, if the filler is placed too far back or off-center, it can create an uneven appearance that draws attention away from the face as a whole.
Dr. Goldfarb notes that when fillers are not placed correctly, they can accentuate signs of aging such as wrinkles and fine lines, making the face appear older than intended.
In some cases, the filler may also cause the skin to become lumpy or bumpy, which can further detract from the desired result.
On the other hand, when chin fillers are used correctly, they can enhance the natural contours of the face and create a more defined jawline, giving the face a more youthful and radiant appearance.
This is particularly true for individuals with a receding chin or a weak jawline, as the filler can help to add volume and definition to these areas.
Furthermore, when used in conjunction with other facial rejuvenation treatments such as Botox and chemical peels, chin fillers can create a comprehensive anti-aging plan that addresses multiple signs of aging simultaneously.
Ultimately, the key to achieving a desirable outcome from chin fillers is proper placement and technique, which requires expertise and experience on the part of the practitioner administering the treatment.
By working with a qualified and experienced healthcare professional, individuals can minimize the risk of adverse effects and maximize the benefits of chin fillers for a more youthful and radiant appearance.
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Now
A balanced facial contour is essential for achieving a youthful and vibrant look, as it defines the overall structure of the face.
Chin fillers, also known as hyaluronic acid fillers, are a popular cosmetic treatment used to enhance the shape and size of the chin. However, one common concern is whether these fillers can actually make you look older instead of younger.
When done correctly, chin fillers can have a rejuvenating effect on the face, particularly around the chin and lower face area. A balanced facial contour is crucial for achieving this youthful and vibrant look.
- A well-defined jawline and chin are essential for creating a harmonious and balanced facial structure.
- Chin fillers can help to create a more defined jawline by filling in any recesses or hollows, which can contribute to a softer, less angular appearance.
- A plump and well-defined chin can help to draw attention away from fine lines and wrinkles on the lower face area.
However, if not done correctly, chin fillers can actually have an opposite effect. Overfilling or placing too much filler in one area can lead to an unnatural and aged appearance.
- Overfilling can result in a “boxy” or “puffy” appearance around the mouth and jawline, giving away the youthful effect.
- A poorly placed chin filler can also accentuate fine lines and wrinkles on the lower face area, rather than diminishing them.
It’s also worth noting that a balanced facial contour is not just about the shape of the chin; it’s also about the overall structure of the face. A harmonious balance between the eyes, nose, mouth, and jawline is essential for creating a youthful and vibrant look.
- The distance between the nose and the upper lip should be in proportion to the rest of the face.
- The shape and size of the ears should complement the rest of the facial structure.
In conclusion, when done correctly, chin fillers can have a rejuvenating effect on the face, particularly around the chin and lower face area. A balanced facial contour is essential for achieving a youthful and vibrant look, but it’s equally important to avoid overfilling or poorly placed fillers that can lead to an unnatural and aged appearance.
Long-Term Effects of Chin Fillers on Aging Appearance
The use of chin fillers has become increasingly popular over the years, particularly among individuals seeking to enhance the definition of their jawline and reduce the appearance of a double chin. However, one common concern associated with chin fillers is whether they can actually contribute to an aging appearance.
When injected into the submental area, chin fillers can temporarily smooth out fine lines and wrinkles, giving the skin a plumper and more youthful appearance. However, if used in excess or improperly, these fillers can have unintended consequences that may accentuate signs of aging.
One of the long-term effects of chin fillers is the risk of developing chronic puffy-looking skin in the treated area. This occurs when the body reacts to the foreign particles within the filler material, causing inflammation and swelling that can persist for extended periods.
Persistent puffiness can be particularly concerning, as it can give the appearance of a permanently swollen or sunken chin. In some cases, this condition may even lead to the formation of unsightly bruises or discoloration around the treated area.
Inadequate use of chin fillers can result in a loss of facial contour, particularly if too much filler is injected into the submental area. This can lead to an unnatural appearance, where the jawline appears softer or less defined than it naturally would.
Furthermore, overuse of chin fillers can also cause the skin to lose its natural elasticity and firmness, leading to a saggy or aged appearance in the surrounding areas.
The redistribution of natural fat is another potential long-term effect of chin fillers. When fillers are used to augment the submental area, they can stimulate the body to redistribute fat cells in that region, leading to an uneven or lumpy appearance.
This condition, known as atrophy or lipodystrophy, can be particularly problematic if it occurs in areas where the skin is thin or fragile. In some cases, natural fat may even accumulate in other areas of the face, such as around the eyes or cheeks, creating an uneven and aged appearance.
The use of chin fillers can also lead to temporary paralysis of the muscles in the treated area. This occurs when the filler material is injected into the nerve endings surrounding the muscle tissue, causing numbness or weakness that may last for several weeks.
In some cases, this condition can be more severe and persistent, leading to permanent nerve damage or changes in facial movement patterns.
The long-term effects of chin fillers can also lead to a range of other complications, including infections, allergic reactions, and scarring. In rare cases, more serious complications such as facial asymmetry or nerve damage may occur.
It is essential to consult with a qualified and experienced healthcare professional before undergoing any cosmetic treatment, including the use of chin fillers. By taking the necessary precautions and following proper injection techniques, individuals can minimize the risk of adverse effects and achieve optimal results from their treatment.
The effects of long-term use of chin fillers can be quite dramatic, and it’s essential to consider these potential consequences when making a decision about undergoing this cosmetic treatment.
Repeatedly using chin fillers can lead to the formation of excess collagen and elastin in the skin, resulting in a puffy or lumpy appearance.
This chronic inflammation can cause scarring and the formation of keloid formations, which can be permanent.
Furthermore, the constant injection of fillers into the skin can lead to the creation of fibrotic tissue, causing the skin to become thickened and leathery.
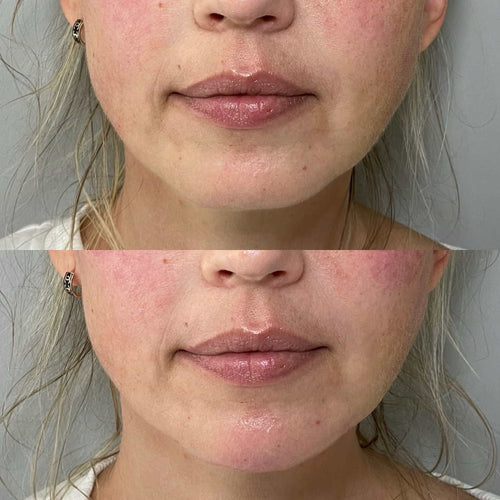
Over time, this can result in a loss of facial elasticity, leading to sagging of the skin around the mouth, chin, and jowls, all of which are characteristic features of aging.
Additionally, the repeated use of fillers can cause damage to the surrounding tissue, including nerves and blood vessels, which can lead to numbness, tingling, or even permanent nerve damage.
Research has also shown that chin fillers can affect the facial skin’s ability to produce collagen naturally, leading to a decline in skin quality and a loss of volume over time.
This can cause the face to take on a more aged appearance, with a sunken or hollow look under the eyes, as well as a loss of definition around the mouth and jawline.
Furthermore, the use of chin fillers has been linked to an increased risk of skin infection, which can be serious in some cases.
The long-term effects of chin fillers on aging appearance are not limited to physical changes; they can also affect a person’s mental health and self-esteem.
Repeatedly using fillers can lead to a cycle of repeated injections and surgeries, which can cause emotional distress and anxiety about the outcome.
It’s essential to weigh these potential risks against the benefits of chin fillers before making a decision about undergoing this treatment.
A comprehensive discussion with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist is crucial in determining whether chin fillers are right for you, as well as exploring alternative treatments that may be more suitable for your individual concerns and needs.
Ultimately, the long-term effects of chin fillers on aging appearance highlight the importance of carefully considering all aspects of cosmetic treatment before making a decision.
The use of *_chin fillers_* has become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly among individuals seeking to enhance their facial appearance and reduce signs of *_aging_*. However, a study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology raises concerns about the long-term effects of repetitive injections on the aging appearance.
The study found that patients who received repeat injections for the same area experienced *increased skin thickness* over time. This can lead to an unnatural and *over-filled* appearance, which can be detrimental to one’s overall facial contour.
The researchers noted that repeated injections of *_chin fillers_* can cause a range of issues, including *hypertrophy*, or the growth of excess tissue under the skin. This can result in an uneven and *sagged* appearance, particularly around the jawline and neck.
Furthermore, the study highlighted that *repeated injections* of *_chin fillers_* can lead to a decrease in facial contour. This is due to the accumulation of fat beneath the skin, which can cause the face to appear more rounded and less defined.
The use of *_chin fillers_* was also found to increase the risk of *_skin atrophy_*, or the thinning of skin tissue. This can lead to a lumpy or *atrophic* appearance, particularly in areas where repeated injections have been administered.
It is essential for individuals considering *_chin filler_* treatment to be aware of these potential risks and to discuss their options with a qualified and experienced practitioner. They should also be aware that the results of *_chin filler_* treatment are not permanent and may require repeat injections over time.
Ultimately, while *_chin fillers_* can provide temporary improvements to facial appearance, the long-term effects of repetitive injections on the aging process cannot be ignored. Individuals seeking to address signs of *_aging_* should consider alternative treatments, such as *_non-surgical face lifts_* or *_botulinum toxin_* injections, which may offer more sustainable and effective results.
In order to truly evaluate the long-term effects of chin fillers on aging appearance, it’s essential to consider the nuances of facial structure and the natural aging process.
As we age, the face undergoes a series of subtle changes that can be influenced by the judicious use of cosmetic injections like chin fillers. These changes can include a loss of volume in the mid-face, particularly around the cheekbones and jawline, as well as the formation of nasolabial folds and marionettes lines.
Chin fillers are used to restore lost facial contour and enhance the definition of the jawline. However, when used excessively or with a lack of care, chin fillers can accentuate wrinkles and sagging skin, ultimately contributing to an older appearance.
Dr. David L. Bank, a professor at Georgetown University, emphasizes the importance of careful injection technique and realistic expectations when undergoing chin fillers. According to Dr. Bank, “the key to successful chin filling is not just about injecting the right amount of filler, but also about placing it in the correct location and using a balanced approach that considers the individual’s facial structure and aging patterns.”
When done correctly, chin fillers can effectively restore lost volume and create a more defined jawline, reducing the appearance of sagging skin and wrinkles. However, even with proper technique, the longevity of results from chin fillers varies depending on several factors, including the individual’s lifestyle, facial anatomy, and filler material used.
Over time, the effects of chin fillers can be affected by gravity, muscle activity, and metabolic processes. Filler materials, such as hyaluronic acid and calcium hydroxylapatite, tend to break down at varying rates, requiring repeat treatments to maintain optimal results.
To mitigate these effects and preserve a youthful appearance, it’s crucial to work with an experienced and skilled injector who has a deep understanding of facial anatomy and aging patterns. Regular maintenance treatments, combined with healthy lifestyle habits such as sun protection and regular exercise, can also help extend the longevity of chin filler results.
Ultimately, the long-term effects of chin fillers on aging appearance depend on a combination of factors, including the quality of the procedure, individual anatomy, and post-treatment care. By adopting a balanced approach to facial rejuvenation and working with a skilled injector, it’s possible to achieve natural-looking results that enhance the overall contours of the face without accentuating signs of aging.
It’s also worth noting that alternative treatments, such as thread lift or facelifts, may be more suitable for individuals seeking long-term facial rejuvenation. These procedures address deeper structural issues and can provide more substantial and lasting results compared to chin fillers alone.
In conclusion, while chin fillers can effectively enhance the definition of the jawline and restore lost volume, their long-term effects on aging appearance depend on careful injection technique, realistic expectations, and a comprehensive understanding of facial anatomy and aging patterns. By working with an experienced injector and adopting a balanced approach to facial rejuvenation, individuals can achieve natural-looking results that promote a youthful and refreshed appearance.
Read more about Market Day ME here. Read more about Goonie Yoga and Therapy here. Read more about One One Three Online here.









